
Ayurveda is an amalgamation of various aspects of life. Be it physical, psychological, social or spiritual, all these four aspects of life are mentioned in detail in Ayurveda. Thus, it is also known as the “science of life”.
Our questions regarding life such as how to attain a happy life, what is a sad life, and how to remove sadness and bring happiness, all are answered by Ayurveda. Not just this, but any other issue that bothers you regarding life can be answered by Ayurveda. The term “Ayurveda” is made up of two different terms i.e., “ayuh” meaning life, and “Veda” meaning science, thus, Ayurveda is known as the “science of life”.
Historians, archaeologists, and medical experts derive information about Ayurveda from ancient Vedic texts. These texts contain information about Ayurvedic treatments and how Ayurvedic medicines help in improving health and lifestyle. Ayurveda originated in India as a system of medicine and it has significance to date.
Ayurveda’s origin is attributed to Atharva Veda who mentions various diseases that human beings face and how they can be treated.
There are a total of eight branches of Ayurveda. These eight branches are also referred to as “the eight limbs of Ayurveda” or “Ashtanga Ayurveda”. The term “Ashtanga” is an amalgamation of two terms i.e., “ashta” which means eight, and “anga” which means branches or limbs.
Every branch of Ayurveda has its own significance and is often studied and specialized separately. Nowadays, students who are interested in Ayurveda or any of its branches can pursue it as a degree. The Mansarovar Ayurvedic Medical College in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh provides a Bachelor’s degree in Ayurveda, Medicine, and Surgery and Post Graduate degrees.
Also Read: Know all about the BAMS course - Admission details, Syllabus and Career Options
Here are the eight branches of Ayurveda:
The term “Kaya Chikitsa” means “treatment of diseases of the entire body”. Hence, this branch provides information on diseases that affect the body such as fever, bleeding disorders, consumption, memory issues, skin-related problems, urinary disorders, etc. “Kaya” also means “antaragni” i.e., the fire of the physical body. So, Kaya Chikitsa suggests that the fire within the physical body should be well-maintained as it is responsible for the transformation and conversion of body cells and tissues. In case the innate fire isn’t controlled then it can lead to various diseases like fever, skin issues, bleeding problems, etc.
This branch of Ayurveda is also named Koumara Bhritya. This specific branch specializes in the nutrition of children. The Diet of children, how to purify milk, and how to treat diseases that occur in children are all mentioned in this specific division.
Also known as “Bhuta Vidya”, this branch concentrates on diseases and problems caused by various grahas like Deva or god, Daitya or monster, Gandharva or singers from heaven, Yaksha or demigods, Rakshasa or demon, Pitru or ancestral forefathers, Pisachi or devils, etc.
This branch of Ayurveda deals with diseases and treatments of the body parts that are above the collar bone. These body parts include the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, nose, and neck. It is also named Shalakya Tantra. The term “urdhwanga” is made up of two words- “urdhwa” which means upper and “anga” which means organs.
The shalya tantra branch of Ayurveda includes various methods through which “shalya” i.e., foreign objects are removed from the body. These foreign objects include gravel, wood, dust, pus, contaminated wounds, etc., and can be a root cause of various diseases. It also includes the study and cure of Ama Vrana or immature wounds, Pakva Vrana or mature wounds, etc. Further, this subdivision also elaborates on Yantras or instruments, Shastra or surgical instruments, Agni Karma, etc.
This particular branch of Ayurveda is also known as Visha Shikitsa which means “treatment of poison”. Hence, it focuses on methods of treating bites and stings of various insects, rodents, and snakes which can transfer the poison to human beings. It also elaborates on the various types of poisons, their consequence and how to heal them. These are Swabhavika Visha or natural poison, Kritrima Visha or artificial poison, and Samyoga Visha or a combination of poisons to name a few.
Also known as Rasayana Tantra, this branch provides knowledge on how to remain young for a longer duration, how to prevent ageing, and how to elongate your life span, intelligence, and immunity. This branch also discusses how to prevent disease in the later part of life i.e., during old age and how to prevent premature ageing.
Also Read: Aging Better with Ayurveda
The eighth branch of Ayurveda talks about methods that can be used to nourish, cleanse and improve the quantity and production of semen in those who deal with problems such as Alpa Shukra or scanty semen, Ksheena Shukra or decreased semen, Dushta Shukra or contaminated semen, etc. This branch also discusses how to increase someone’s interest in sex.
The MAMC college in Bhopal was conceived in 2015 by Sri Sai Gramothan Samiti. The institute promises to provide best-in-class education in Ayurveda. Along with that, they train students in skilled work and provide art facilities so that the students come out as learned professionals in the field of Ayurveda.
Under the undergraduate category, the institute provides a Bachelor of Ayurveda, Medicine, and Surgery. To be qualified to get admission in the course, the student must have passed class 12th or intermediate with Physics, Chemistry, and Biology with a minimum of 50% for the general category and 45% for SC, ST, and OBC categories. The candidate must have qualified NEET, age should be between 17 and 25 years as on 31st December of the year in which they are taking admission. In case the student is eligible, admission will be given after the relevant Central/State government counseling. The course is of 4.5 years and another year of rotatory internship.
At the post-graduation level, provides the following courses:
MD/MS (05 Seats in each subject)
To be eligible to study the post-graduation course, the candidate must have pursued BAMS from a recognized university, and he/she must have qualified AIA-PGET exam. If the student is eligible, admission will be given after the relevant Central/State government counseling. The course will be of a duration of 3 years.
Thus, if you wish to study Ayurveda, you must consider MAMC college in Bhopal. It is one of the best private medical institutes to study Ayurveda.
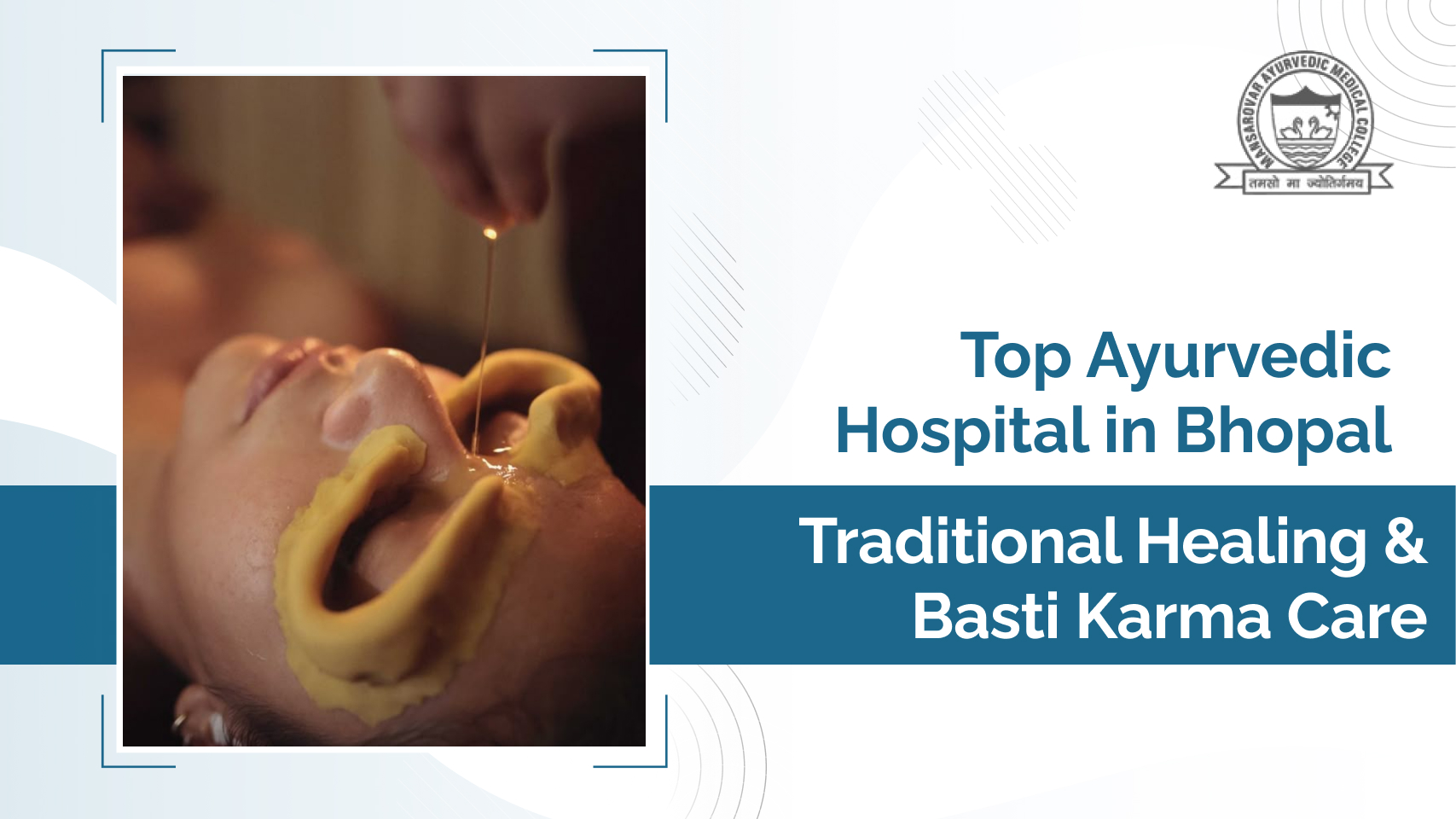
Experience Authentic Healing at a Renowned Ayurvedic Hospital in Bhopal

Experience Healing at the Best Ayurvedic Hospital in India

Experience Expert Shalya Tantra Care at Best Ayurvedic Hospital in India

Healing Naturally at the Best Ayurvedic Hospital in Bhopal

Obesity Treatment in Ayurveda: A Natural & Holistic Approach to Weight Loss

Vata Dosha in Ayurveda - Meaning, Causes, Diet Plan & Treatment

Complete Guide to Panchakarma Treatment: Ayurveda’s Deep Cleansing Therapy

Basti Panchkarma Therapy – Ayurvedic Basti Treatment Benefits

Top Nasya Treatment Benefits You Should Know

Explore the Panchakarma Treatment Benefits

BAMS Colleges in Madhya Pradesh – Choose Excellence in Ayurveda

Best Ayurvedic College in India – Why Choose MAMC Bhopal

Best Private Ayurvedic College in Bhopal: Top Colleges for Ayurvedic Studies in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh

Best BAMS Colleges in Madhya Pradesh

Can Ayurveda Support Women's Health at Every Stage of Life?

How BAMS Courses Prepare Students for a Dynamic Career in Ayurveda

How Ayurveda Aligns Mind, Body, and Spirit for Optimal Health

Is Ayurvedic College Right for You? Exploring Your Options

Is Choosing a Private College for Obtaining a BAMS Beneficial?

10 Benefits of Having an Ayurveda Degree